
Today in 1988, US Patent 4729900 A was issued, an invention of Kenneth Clare, Margaret A. Lawson, and Walter Bryden, assigned to Merck & Co., Inc., for their “Foam-Stabilized Malt Beverage.” There’s no Abstract, although in the description it includes this summary:
A fermented malt beverage having improved foam stability and desirable lace, cling, and clarity is described. The beverage is stabilized by adding 5-400 ppm by weight of combined xanthan gum and a cold-water soluble protein.
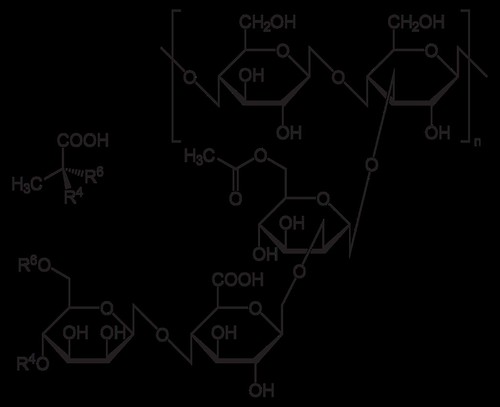
Here’s a better explanation, from the application:
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
A number of malt beverages or beers will produce a relatively good foam immediately after pouring, but the foams so produced are not as persistent as is usually desired by the consumers of such products. In addition, consumers desire a beer possessing a foam that will “cling” to the insides of a glass or mug in an attractive “lacy” pattern. Lace and cling are difficult to achieve in the presence of slight contaminant levels of surfactants or detergents on the glassware, as occurs when beer mugs or glasses are handwashed and quickly rinsed prior to use. A further requirement is that the beer exhibit good clarity to the consumer, i.e., the absence of any noticeable “haze”.
Propylene glycol alginate (PGA), heteropolysaccharide S-10 (see U.S. Pat. No. 3,966,976) and cellulose ether (see U.S. Pat. No. 3,669,00) are additives known to stabilize beer foam.
However, continuing research is being conducted in an effort to discover new polymers, additives, and polymer combinations which may be more economical and which can be utilized to impart improved foam stability, lace and clarity to fermented malt beverages while avoiding attendant “haze” levels.
Xanthan gum as an extender or thickener in the food industry is well described in the literature. Also well known in the art is the use of collagen hydrolysates, derived from animal skin, in the preparation of hair care preparation, shampoos and skin care preparations. Collagen derivatives have been used in the brewing process as fining agents. Further, gelatin hydrolysates are well known in the pharmaceutical industry as tablet excipients used in granulating and binding operations during tablet manufacture. However, there are no general references to such compositions in combination being disclosed for specifically improving foam stability and properties of fermented malt beverages.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
It has now been found that the foam retention and lace/cling properties of a fermented malt beverage can be stabilized while minimizing haze formation by adding a combination of xanthan gum and cold-water soluble protein to the beverage in a combined amount sufficient to result in a final concentration in the beverage in the range of about 5-400 ppm, by weight. The proteins useful in the invention include, inter alia, collagen, gelatin, or milk protein hydrolysates, having a number average molecular weight of 900-12,000, which can be used in a weight ratio of 1:4 to 4:1 of xanthan gum/protein.

