![]()
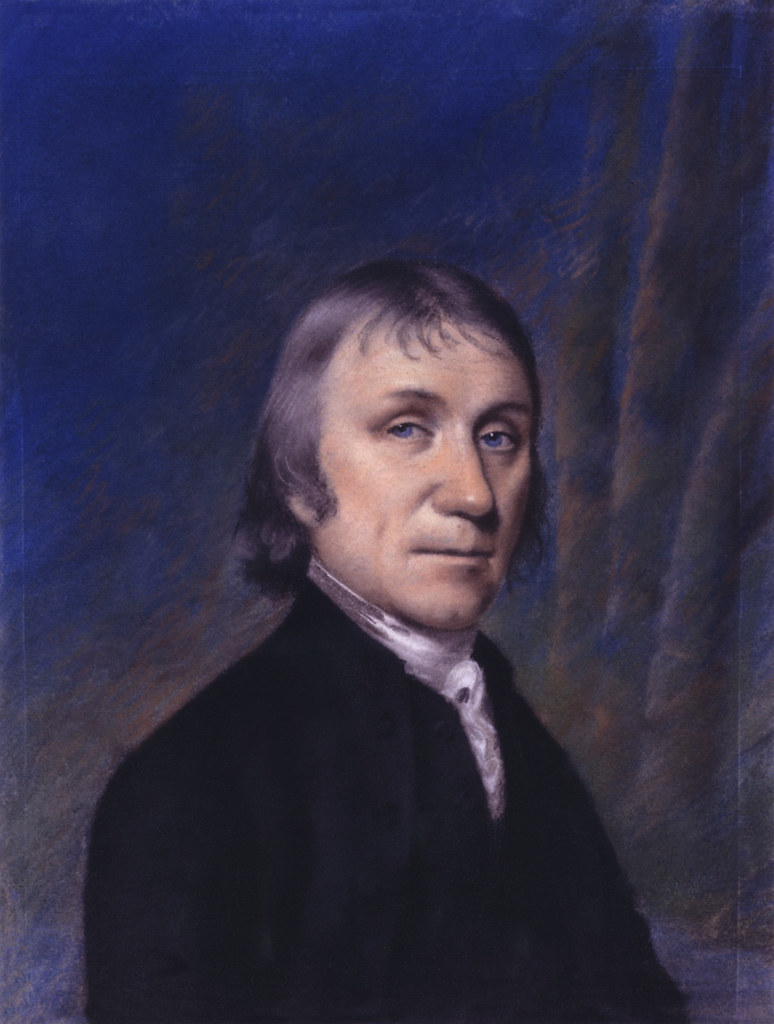
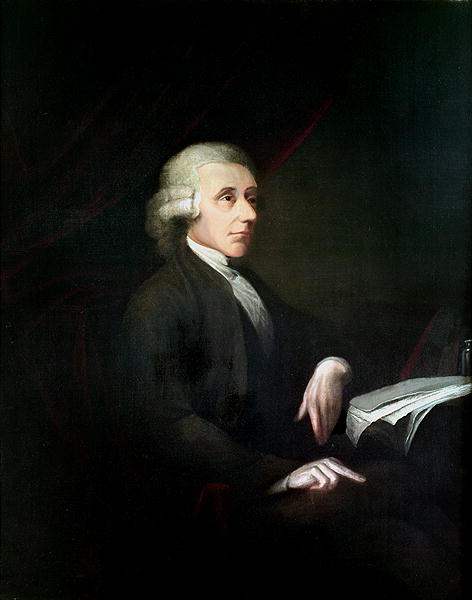
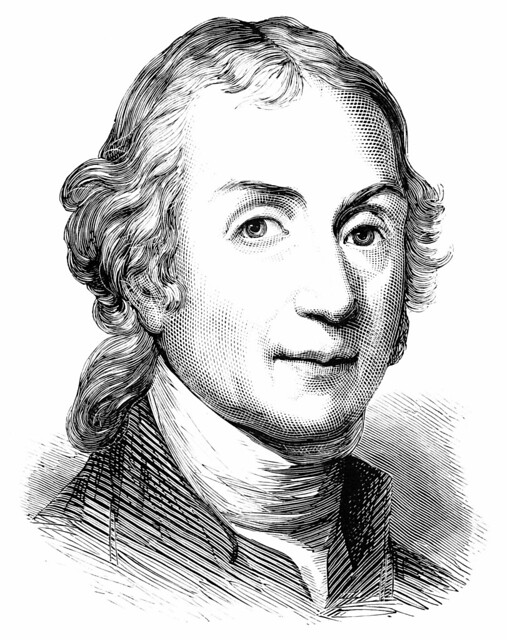
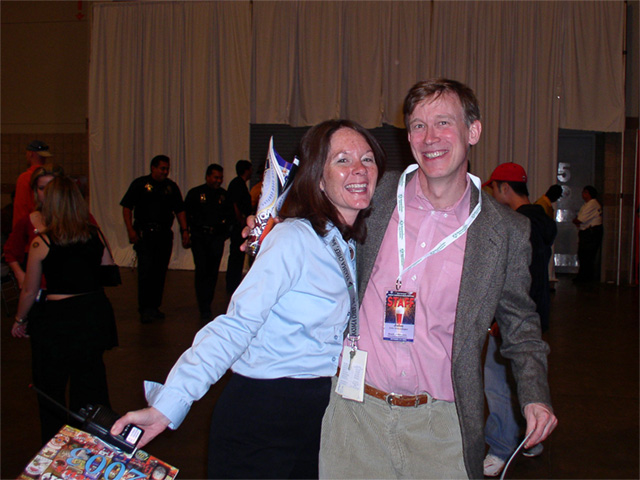
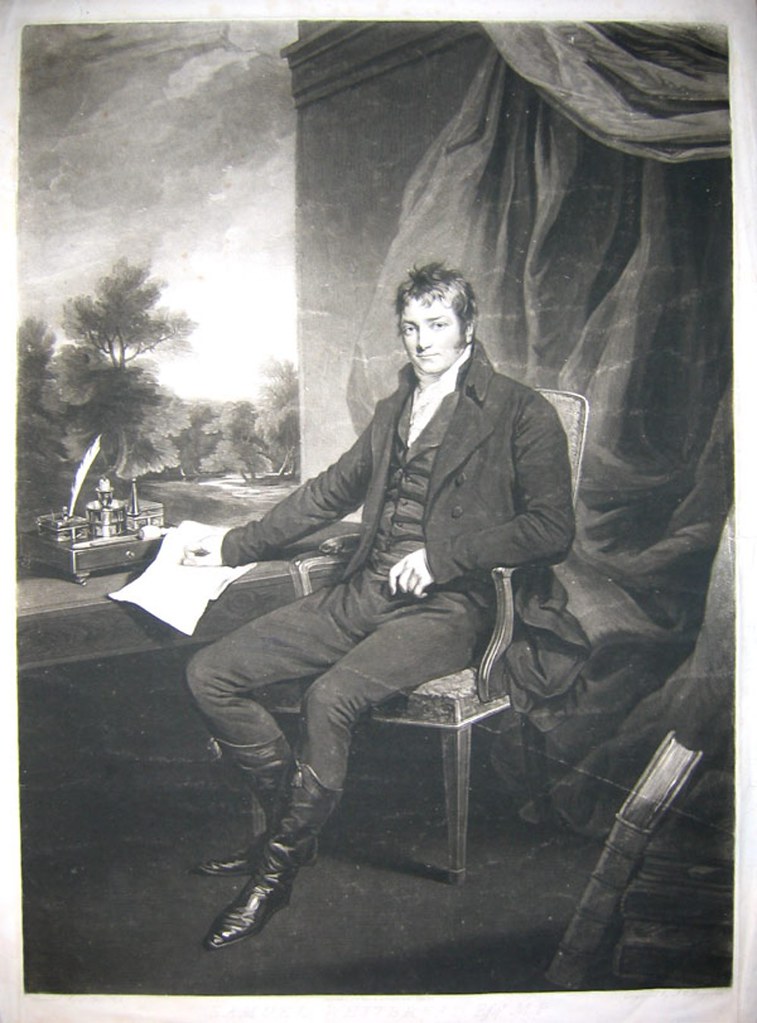
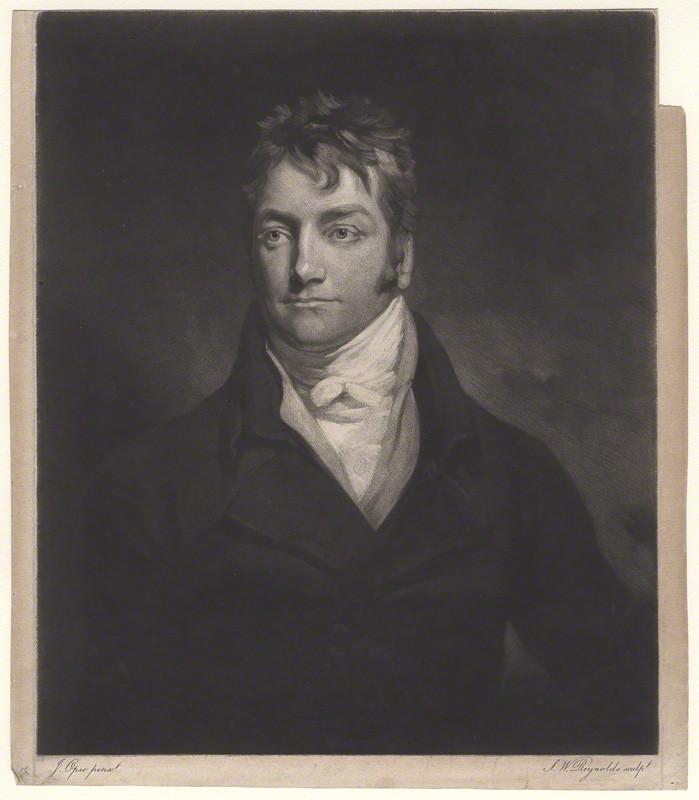
Today is the birthday of Alan MacGregor Cranston (June 19, 1914–December 31, 2000). Cranston was a Democratic senator from California, born in Palo Alto, and served four terms.
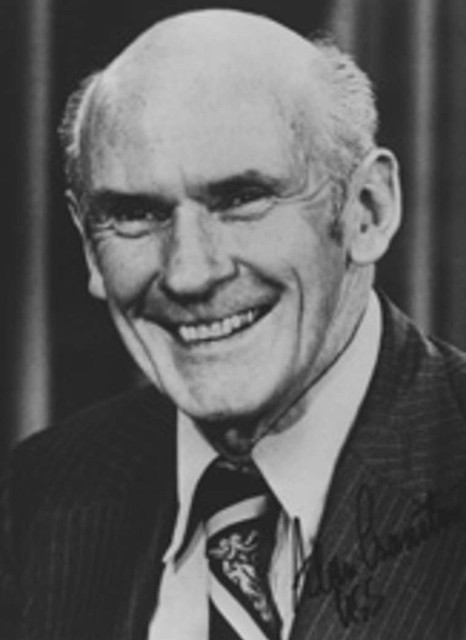

Here’s a biography from Find a Grave:
US Senator. A member of the Democratic party, he represented the state of California for four terms in the US Senate from January 1969 until January 1993, serving as the Democratic Whip from 1977 until 1991. Born Alan MacGregor Cranston in Palo Alto, California into a wealthy real estate family, he attended local public schools before attending Pomona College in Claremont, California and the Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico in Mexico City, Mexico, and graduated in 1936 from Stanford University in Palo Alto with a degree in journalism. In 1937 he became a correspondent for the International News Service for two years preceding World War II, covering Europe and North Africa. When an abridged English-language translation of Adolf Hitler’s “Mein Kampf” was released, sanitized to exclude some of Hitler’s anti-semitism and militancy, he published a different translation (with annotations) which he believed more accurately reflected the contents of the book. In 1939 Hitler’s publisher sued him for copyright violation in Connecticut and a judge ruled in Hitler’s favor and publication of the book was halted. From 1940 until 1944 he served as chief, foreign language division in the Office of War Information and in 1944 he enlisted in the US Army. In 1945 he wrote the book, “The Killing of the Peace,” a synopsis of the failed bid to get the US to join the League of Nations immediately following World War I. A world government supporter, he attended the 1945 conference that led to the Dublin Declaration, and became president of the World Federalist Association in 1948. In 1949 he successfully pushed for the California legislature to pass the World Federalist California Resolution, calling on Congress to amend the Constitution to allow US participation in a federal world government. From 1949 until 1952 he was the national president of the United World Federalists. In 1952 he co-founded the California Democratic Council and served as its chairman. In 1958 he was elected California’s State Controller as a Democrat and was re-elected in 1962. In 1968 he ran as the Democratic candidate for US Senate and was elected to the first of four six-year terms, defeating Republican challenger Max Rafferty, followed by Republican challenger H.L. “Bill” Richardson in 1974, Republican Paul Gann in 1980, and Republican Congressman Ed Zschau in 1986. During his time in the US Senate, he served on the Banking, Housing, Urban Affairs, Veterans (which he chaired), and Foreign Relations Committees and was strongly opposed to the US involvement in the Vietnam War. He was an unsuccessful candidate for the 1984 Democratic presidential nomination, dropping out of the race after finishing poorly in the Iowa and New Hampshire primaries. In November 1991 he was reprimanded by the US Senate Select Committee on Ethics for “improper conduct” after Lincoln Savings head Charles Keating’s companies contributed $850,000 to voter registration groups closely affiliated with him. Because the Keating affair had damaged his political career, coupled with his diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer, he decided against running for a 5th US Senate term. His final act as a Senator was to preside over the inauguration of Bill Clinton as President of the US on January 20, 1993. A fitness enthusiast, he was notable for practicing and participating in the sport of track and field as a sprinter in special senior races. An avid lifetime supporter of the global abolishment of nuclear weapons, in his retirement he became a part of the Nuclear Weapon Elimination Initiative of the State of the World Forum and founded the Global Security Institute in 1999, serving as its president. He died of natural causes in Los Altos, California at the age of 86.

Of course, the one thing left out of Cranston’s biography in most accounts is the reason that he’s featured here. On January 4, 1977, Representative William A. Steiger (Republican from Wisconsin’s 6th District) introduced H.R.1337 a transportation bill with the title “A bill to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1954 with respect to excise tax on certain trucks, buses, tractors, etcetera.”
To that bill, senator Cranston added a crucial amendment which had a profound effect on the landscape of beer today, and its final title was “An Act to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1954 with respect to excise tax on certain trucks, buses, tractors, et cetera, home production of beer and wine, refunds of the taxes on gasoline and special fuels to aerial applicators, and partial rollovers of lump sum distributions.”
Here’s the text of the beer portion of Amendment 3534, added by Senator Alan Cranston:
(e) BEER FOR PERSONAL OR FAMILY USE. — Subject to regulation prescribed by the Secretary, any adult may, without payment of tax, produce beer for personal or family use and not for sale. The aggregate amount of beer exempt from tax under this subsection with respect to any household shall not exceed —
(1) 200 gallons per calendar year if there are 2 or more adults in such household, or
(2) 100 gallons per calendar year if there is only 1 adult in such household.For purposes of this subsection, the term ‘adult’ means an individual who has attained 18 years of age, or the minimum age (if any) established by law applicable in the locality in which the household is situated at which beer may be sold to individuals, whichever is greater.
As we all know, President Jimmy Carter signed H.R. 1337 into law on October 14, 1978, paving the way for the our modern brewing industry that includes over 700 breweries in California alone, and over 4,000 nationwide. Thanks Alan.

In 1984, Cranston made a failed bid to run for president. I bet he would have gotten the homebrewing vote.