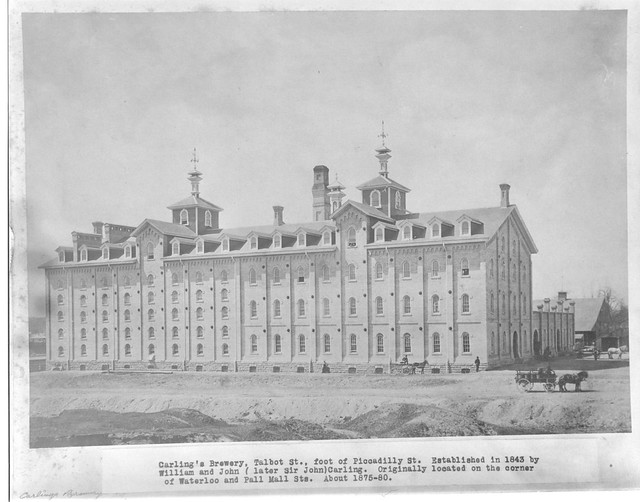
Today is the birthday of John Courage Jr. (June 26, 1788-March 1854). He was the son of John Courage, who founded the Courage Brewery in London in 1787, when he bought a brew house in Horselydown, Bermondsey, London. Junior was born in Southwark, in the London Borough of Southwark, although at least one account states he was born in Aberdeen, Aberdeenshire, in Scotland. Unfortunately, I was unable to find any images of the man himself. When his father died, he was only ten, so the brewery’s manager, John Donaldson, ran the brewery in exchange for a share of the profits. Junior started working at the brewery when he was 16, and seven years later, in 1811, he became a partner in the firm.

This short account of Junior is from Courage & Co.:
The Founder’s son, the second John, entered the Brewery in 1804 aged 16, becoming a partner in 1811. He married Susan Hawes, the daughter of a Norfolk brewer Sidney Hawes in 1823. A copy of an article about Susan’s mother, Elizabeth Hawes (neé Porson) survives in family records. The article states “that Elizabeth was born in 1756, was a servant and a woman of strong natural sense and moral qualities and at night used to sit up in bed reading from the light of a candle volumes of the Universal Magazine. She took in dressmaking and always said she would rise in the world”.

And this is from Geni, a genealogy website:
John Courage (1788-1854) was the only son and eldest child of John Courage (1761-1797), founder of the Courage Brewery, and his wife Harriet.
John Courage senior died in 1797 when his son was only nine or ten years old. Harriet died a year later. On her death, the managing clerk, John Donaldson, took over the running of the Brewery and for a short while the firm was renamed Courage and Donadson.
John Courage junior entered the Brewery in 1804 aged 16, becoming a partner in 1811. In 1851 the business reverted back to solely Courage ownership.
In 1852, a partnership was formed within the Courage family between John (junior – the 2nd) and two of his sons, John (the 3rd) and Robert. On John the 2nd’s death in 1854, John the 3rd took into partnership his brother Edward in 1856 and Henry in 1866.
The Courage Brewery became a limited liability company in 1888.