![]()
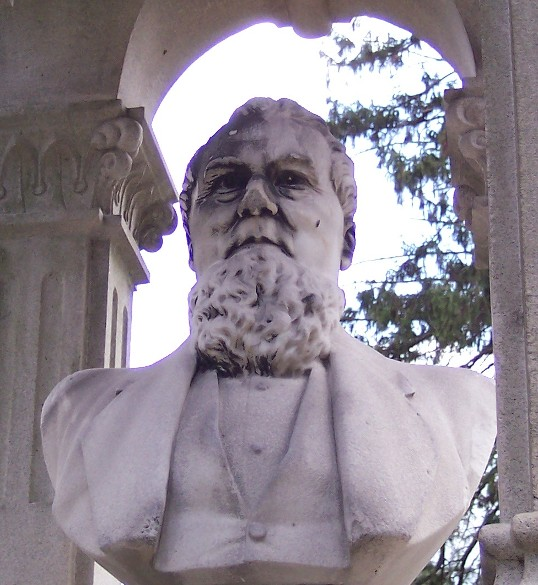
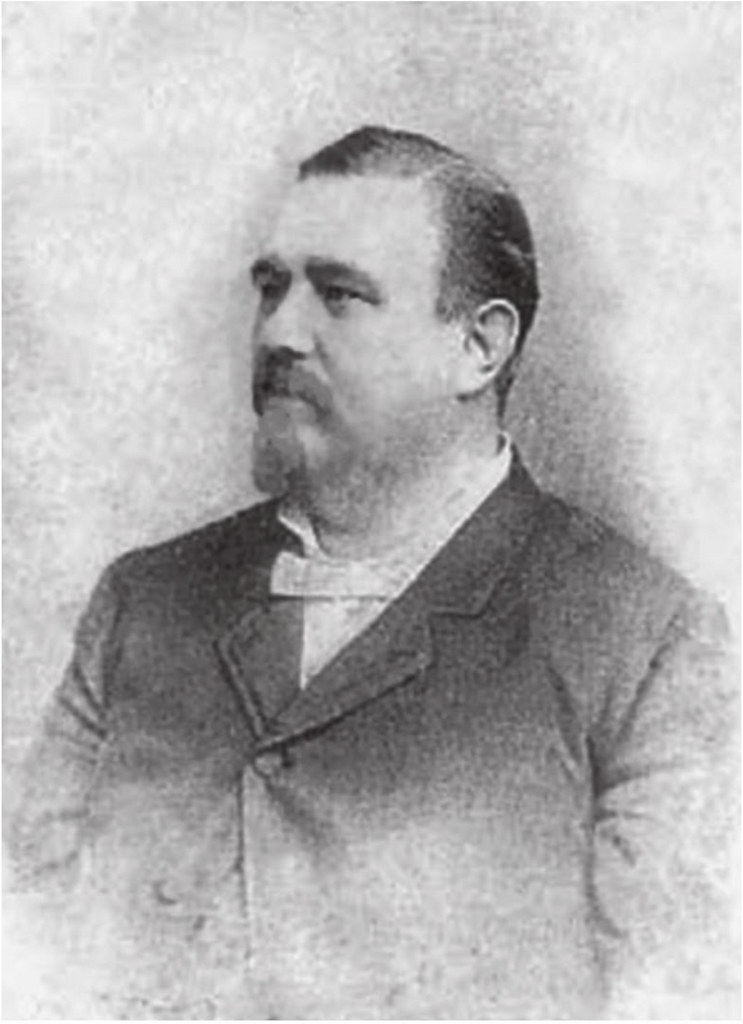
Today is the birthday of Bernhard Stroh (August 20, 1822-June 24, 1882). He was born in Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany, and after a detour in Brazil, emigrated to the U.S. and settled in Detroit.

This biography is from Find-a-Grave:
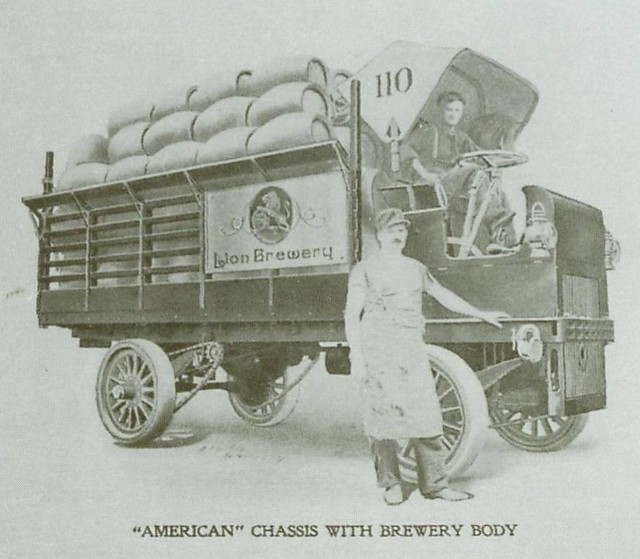
Businessman. He left Germany in 1848, and joined a group of German settlers in Brazil for three years before arriving in America. He landed in Buffalo, New York heading by way of the Erie Canal. The boat he was on docked in Detroit. So Stroh took it upon him self to venture into the city. He liked what he saw and decided to stay. With a few hundred left from the Brazilian business venture he started a small brewery at 57 Catherine Street in Detroit. Soon after establishing his German brewery local patrons in Detroit aquired a desired taste for his German lager beer. Bernhard Stroh would have his sons personally cart small kegs of beer to his customers by wheelbarrow. For over a century now, local Detroiters have enjoyed the same “fire-brewed” taste that the Stroh Family created over 150 years ago.

This is what Wikipedia has to say about Stroh’s early days through Julius Stroh’s tenure:
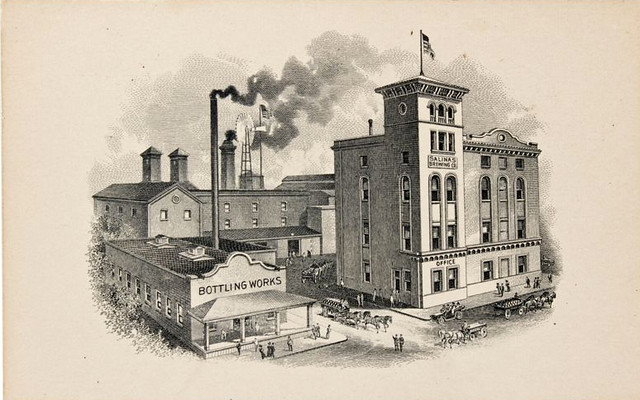
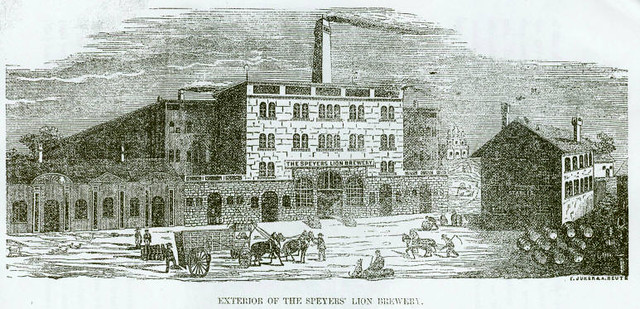
The Stroh family began brewing beer in a family-owned inn during the 18th century in Kirn, Germany. In 1849, during the German Revolution, Bernhard Stroh (1822-1882), who had learned the brewing trade from his father, emigrated to the United States. Bernhard Stroh established his brewery in Detroit in 1850 when he was 28 and immediately started producing Bohemian-style pilsner, which had been developed at the municipal brewery of Pilsen, Bohemia in 1842. In 1865, he purchased additional land and expanded his business and adopted the heraldic lion emblem from the Kyrburg Castle in Germany and named his operation the Lion’s Head Brewery. (The lion emblem is still visible in its advertising and product labels.)
Bernhard Stroh’s original beer selling operation consisted of a basement brewing operation and was then sold door-to-door in a wheelbarrow. The new beer (Stroh’s) sold door-to-door was a lighter-lager beer, brewed in copper kettles.

This short account about Bernhard is from the Entrepreneur Wiki:
The Stroh family has a long history of brewing beer, which first began in Germany. However, due to the German Revolution, in 1849, Bernhard Stroh moved the business to the United States after three years of living in Brazil. He started his company with a budget of $ 150.00.
Stroh selected Detroit, Michigan as the location for his brewery and settled there in 1850. Stroh was 28 years old at the time. The company was known for making a Pilsner (also known as Pilzen) style beer. Pilsner beers are fire-brewed and lighter than traditional beers. In 1855, the company increased in size, and then shortly thereafter became known as Lion’s Head Brewery. The company had been known as Stroh’s Brewery until this time.
The most popular beer sold, Stroh’s, was first peddled via wheelbarrow. The new beer was brewed in copper kettles to enrich the flavor. The company name was then changed to B. Stroh Brewing Company when Bernhard passed in 1882, and his son, Bernhard Junior, took over the business. In 1988, Forbes estimated that the Stroh family had an estimated worth of 700 million dollars. The brewing company stayed in the Stroh family until the year 2000.