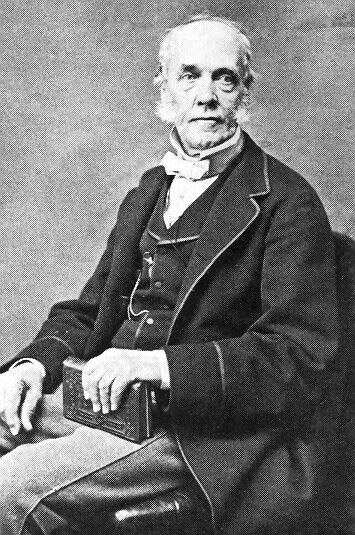![]()
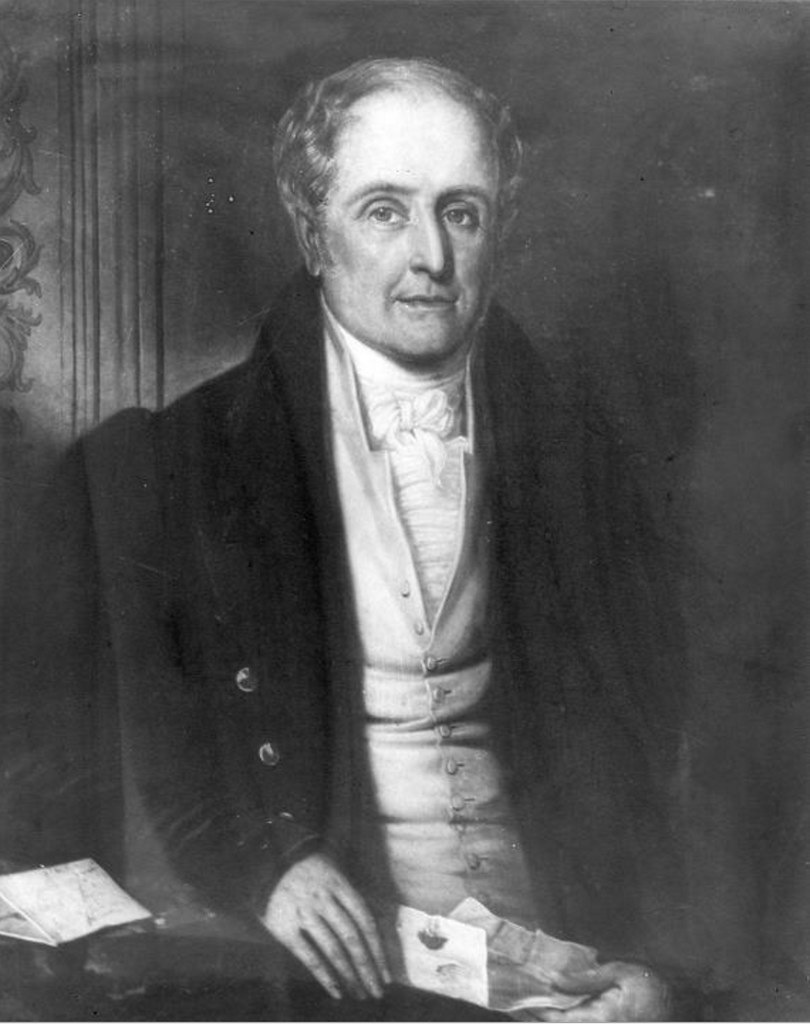
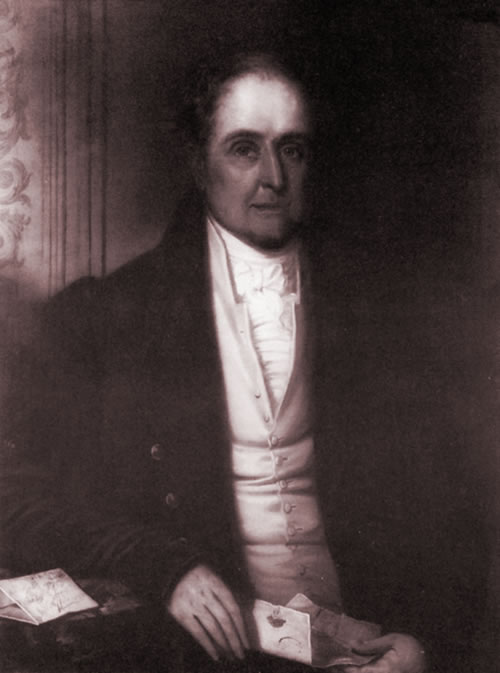
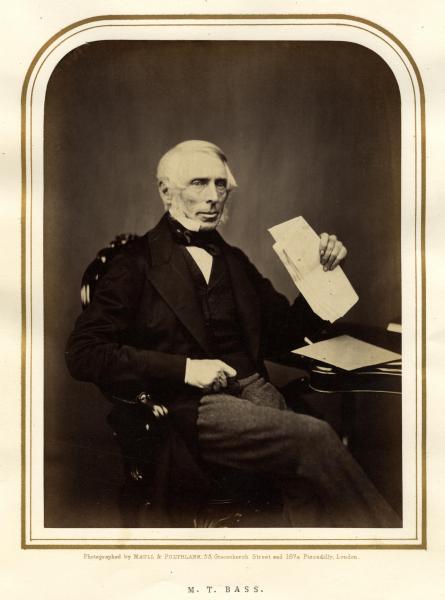
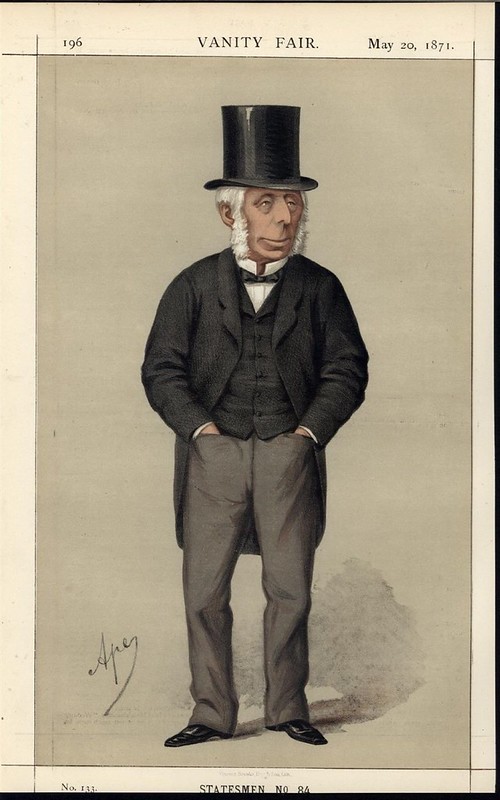
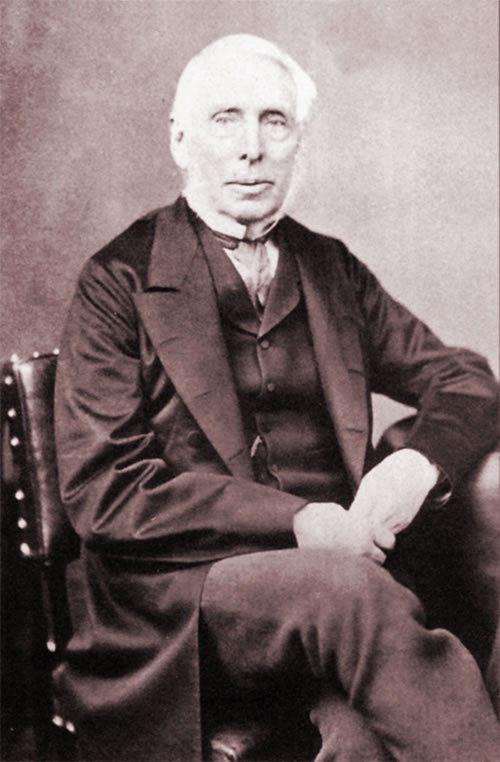
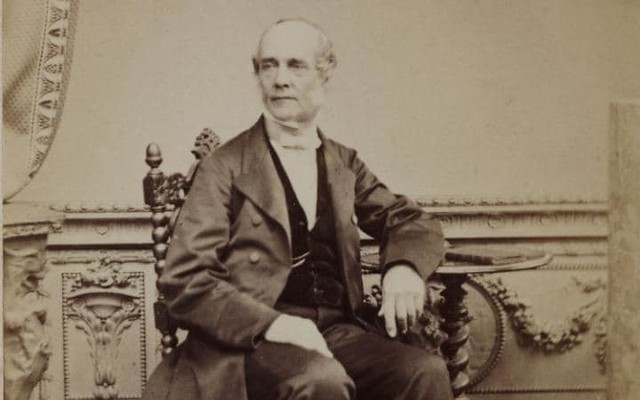
Today is the birthday of Hamar Alfred Bass (July 30, 1842-April 8, 1898). He was the great-grandson of William Bass, the founder of the Bass brewery, and the second son of brewer Michael Thomas Bass.

Here’s his biography from Wikipedia:
Bass was born in Burton upon Trent, the second son of brewer Michael Thomas Bass and his wife Eliza Jane Arden, daughter of Major Samuel Arden of Longcrofts Hall, Stafford. Bass was the great-grandson of William Bass, the founder of the brewery firm of Bass & Co, and his elder brother became Lord Burton. Bass was educated at Harrow School and became a Director of the family firm of Bass, Ratcliff, Gretton and Co. He was Honorary Major of the 4th Prince of Wales’s (North Staffordshire) Regiment and was a J.P. for Staffordshire. Bass played cricket for the Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC), making a single first-class appearance for the MCC against Sussex in 1865. He was dismissed in the MCC’s first-innings by James Lillywhite, while in their second-innings he was dismissed for 3 runs by George Wells. The match ended in a draw.
Bass was elected MP for Tamworth at a in by-election in 1878 and held the seat until 1885 when the representation was reduced to one seat under the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885. He was elected MP for West Staffordshire in the 1885 general election and held the seat until his death aged 55 in 1898 from a complex form of rheumatism.
Bass was a breeder at the Byrkley Stud and his horse “Love Wisely” won the Ascot Gold Cup in 1896. He was also for 12 years master of the Meynell Hunt.
Bass married Louisa Bagot (1853–1942), daughter of William Bagot, 3rd Baron Bagot, in 1879. They lived at Byrkley Lodge and Needwood House, Burton, and also at 145 Piccadilly, London. After his death, Louisa married Rev Bernard Shaw.
Bass’s sister Emily Bass married Sir William Plowden, MP for Wolverhampton West, and his sister Alice Bass married Sir George Chetwode being the mother of Field Marshal Philip Chetwode.
Bass’s son William succeeded in his uncle’s baronetcy according to special remainder. Hamar Bass’s daughter Sibell Lucia married Major Berkeley John Talbot Levett of the Scots Guards, son of Theophilus Levett of Wychnor Park, Staffordshire. Berkeley Levett served as one of the Gentlemen Ushers to the Royal Family from 1919 to 1937.

Back Row: Hon. Col. Legge, Marquis of Soveral, Duchess of Devonshire, Mr Hamar Alfred Bass, Lord Elcho, Miss Jane Thornewill, H.M. Queen Alexandra, Lord Burton (Michael Arthur Bass), Lady Mar & Kellie, Prince Henry of Pless
Front Row: Lady Noreen Bass, Miss Muriel Wilson, Lady Desborough, Lady de Grey, H.M. King Edward VII, Lady Burton (Harriett Bass), Princess Henry of Pless, Mrs Alice Fredrica Keppel, Miss Bunny Thornewill
And this summary is from the Local History of Burton upon Trent:
Hamar Bass was the second son of Michael Thomas Bass and his wife Eliza Jane Arden. He was brother of Lord Burton and also a Director of the family firm of Bass, Ratcliff, Gretton and Co. One sister Emily married Sir William Plowden, MP for Wolverhampton West, and the other married Sir George Chetwode being the mother of Field Marshall Philip Chetwode.
Hamar Bass was MP for Tamworth from 1878 to 1885. He was then MP for West Staffordshire from 1885 until his death aged 56 in 1898 from a complex form of rheumatism.
Hamar Bass married Louisa Bagot (1853-1942), daughter of William Bagot, 3rd Baron Bagot, in 1879. They lived at Byrkley Lodge and Needwood House, Burton, and also at 145 Piccadilly, London. Louisa subsequently married Rev Bernard Shaw. He was a breeder at the Byrkley Stud and his horse “Love Wisely” won the Ascot Gold Cup in 1896. He was also for 12 years master of the Meynell Hunt.
His son William succeeded in his uncle’s baronetcy of Stafford according to special remainder. Hamar Bass’s daughter Sibell Lucia married Major Berkeley John Talbot Levett, Scots Guard, son of Theophilus Levett of Wychnor Park, Staffordshire. Berkeley Levett served as one of the Gentlemen Ushers to the Royal Family from 1919 to 1937.