![]()
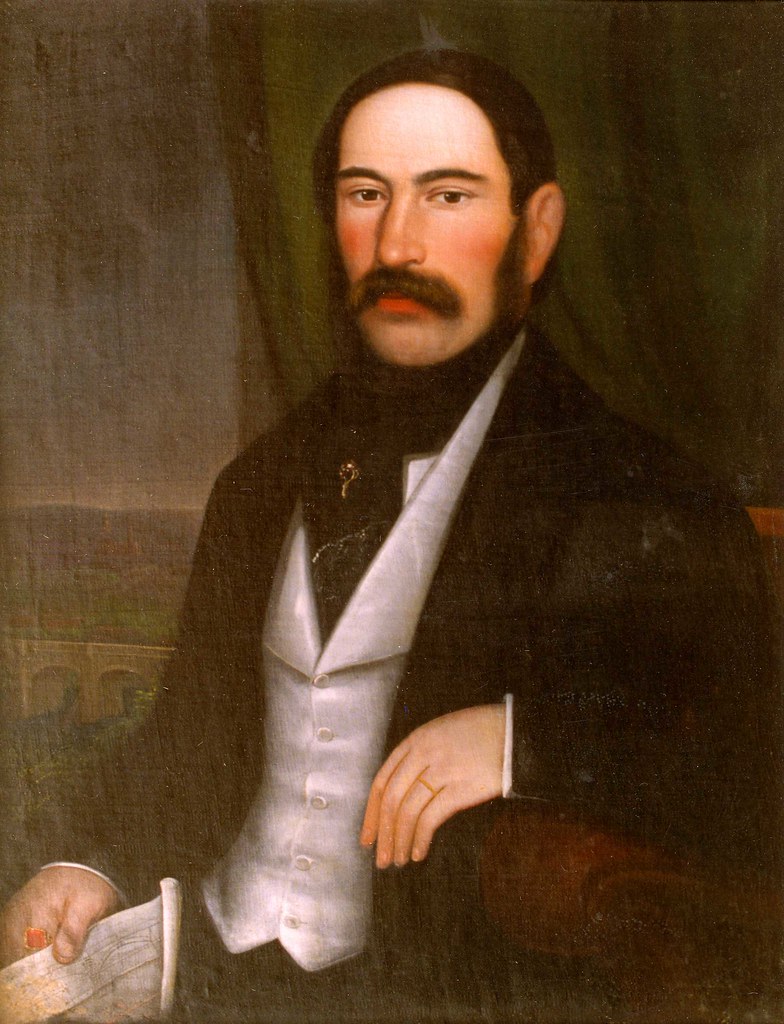
Today is the birthday of William Hoffmeister (January 31, 1827-1902), who was born in Germany, but emigrated to the U.S. in 1847, settling in Cincinnati, Ohio. There in 1856 he founded the William Hoffmeister Brewery, but it was only in production until 1873, when he closed it and opened a saloon. Being open for a mere seventeen years, there’s precious little information about either the brewery or William Hoffmeister, and I was unable to find any picture of him, his beer or his brewery, though this may be his coat of arms.

This is about all I could find on William Hoffmeister, from the Cincinnati Turner Societies: The Cradle of an American Movement, by Dann Woellert, published in 2012.